√100以上 steel yield stress graph 156088
Yield point is well defined and shown on graph for mild steel and it's beyond elastic limit For other materials like copper or aluminum is defined as the point of intersection of stressstrain curve and a line drawn parallel to linear part fron 02 percent deformation (strain ε) and it is also beyond the elastic limitYield Strength Definition Stress Strain Graph Stress Strain Graph Explanation Yield Strength Graph What is Yield Strength?Yield Strength – Yield Point A schematic diagram for the stressstrain curve of low carbon steel at room temperature is shown in the figure There are several stages showing different behaviors, which suggests different mechanical properties To clarify, materials can miss one or more stages shown in the figure, or have totally different stages
Stress Strain Curve Explanation Stages Mild Steel Engineering Intro
Steel yield stress graph
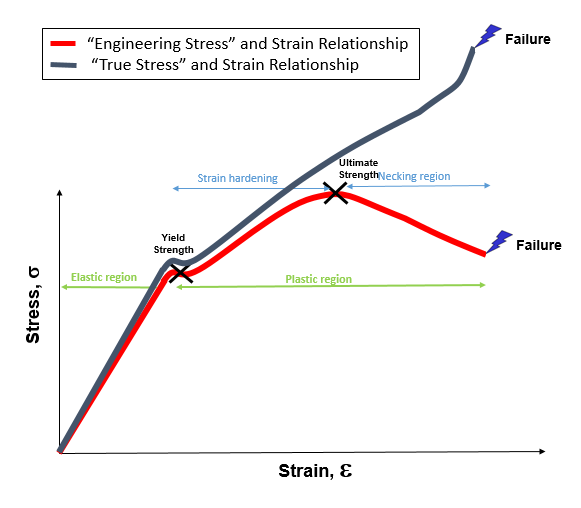
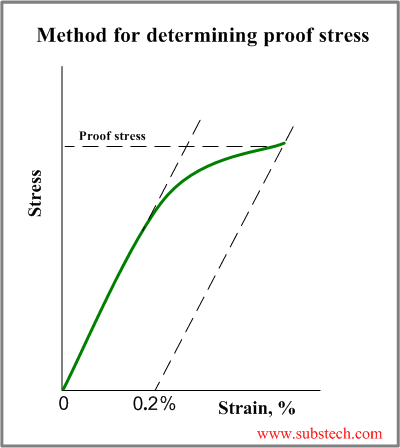
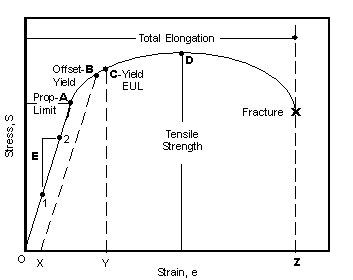
Steel yield stress graph-The StressStrain Graph The strength of a material is determined by a tensile test, a test that requires the material to be mercilessly pulled from its two ends The relationship between the stress to which it is subjected and the strain it consequently suffers can be limned by a graph called the stressstrain curveTherefore, an offset yield point is obtained at a strain of 0002 (02%) A straight line is drawn parallel to initial portion of stressstrain curve at the strain value of 0002 and the point where it intersects the stressstrain curve is taken as yield point True StressTrue Strain



Yield Strength Strength Mechanics Of Materials Engineers Edge
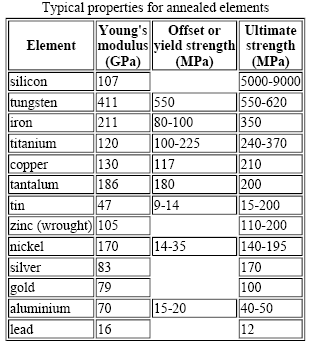
The yield strength at 02% offset is determined by finding the intersection of the stressstrain curve with a line parallel to the initial slope of the curve and which intercepts the abscissa at 02%02% Offset Yield Strength (stress) The stress at the intersection of the stressstrain curve and a straight line with slope of E and beginning at 0002 (02%) on the strain axis The most satisfactory definition of yield strength for aluminum alloys and many other materials Note At this definition of yield, the plastic portion of the strain isStrength is a critical factor in metal uses, for example, some applications require stronger aluminum parts, while some products need high steel hardness or yield strength of steel, this may determine the selection of CNC machining material or product design Here we collect the metal strength chart (tensile, yield strength, hardness, and density included) and mechanical properties chart of
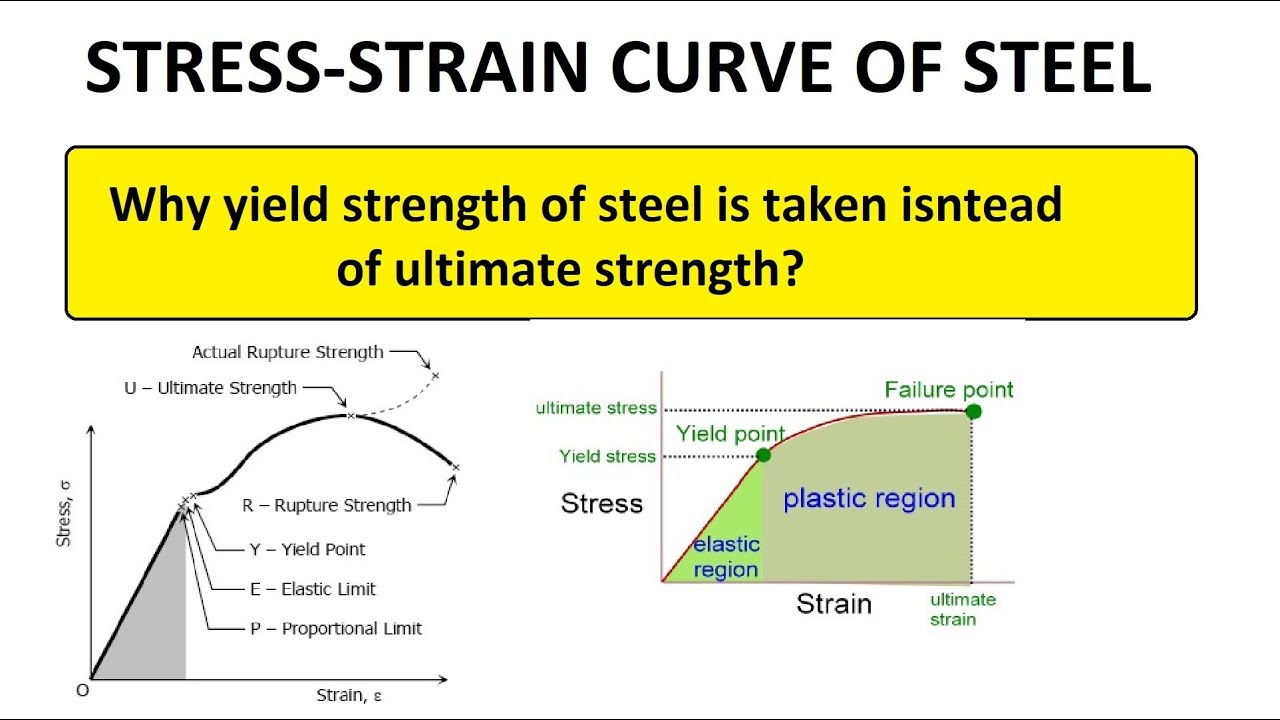
The yield point is the point on a stressstrain curve that indicates the limit of elastic behavior and the beginning plastic behavior Yield strength or yield stress is the material property defined as the stress at which a material begins to deform plastically whereas yield point is the point where nonlinear (elastic plastic) deformation beginsA range of formulas apply to yield stress, including Young's Modulus, stress equation, the 02 percent offset rule and the von Mises criteria Young's Modulus Engineers develop stressstrain curves by performing repeated tests on material samples and compiling the dataTensile / yield strengths and ductilities for some of the plain carbon and low alloy steels are
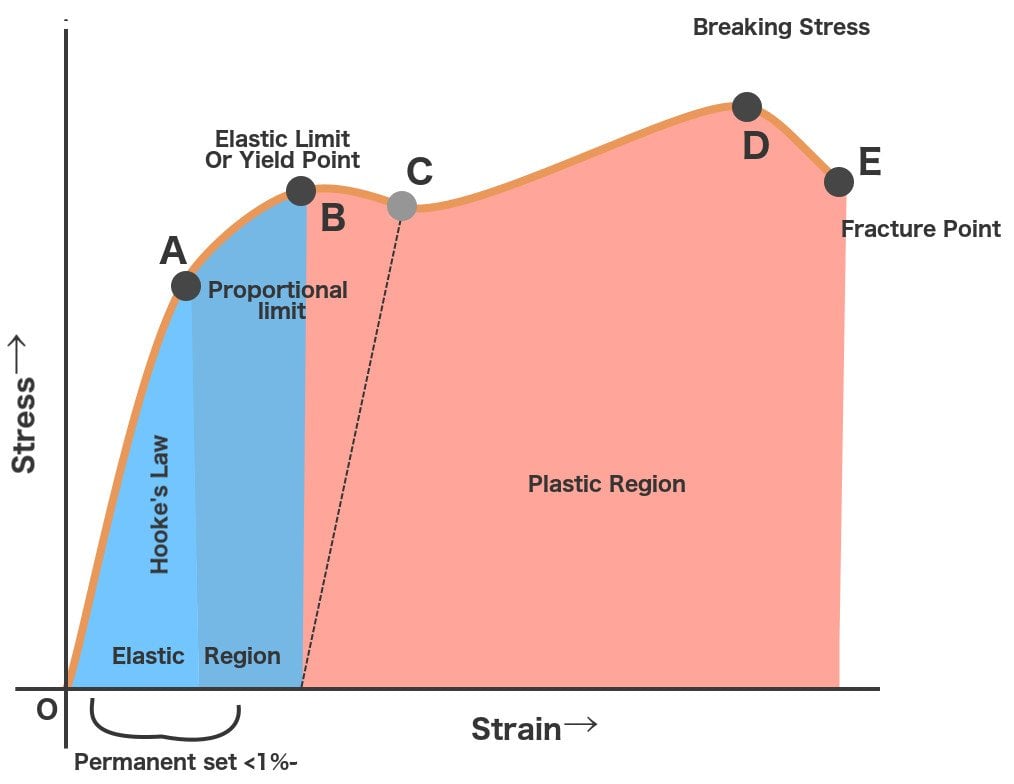
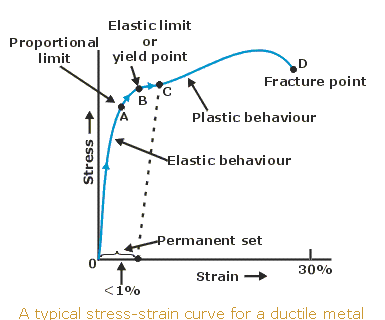
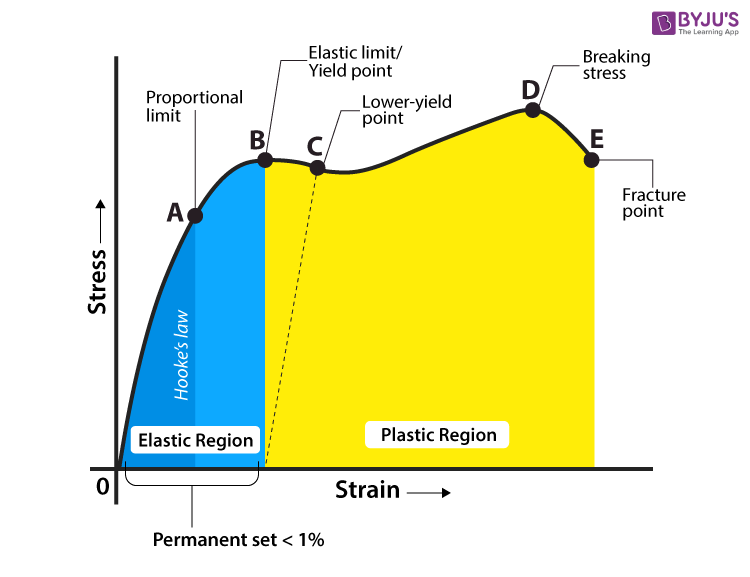
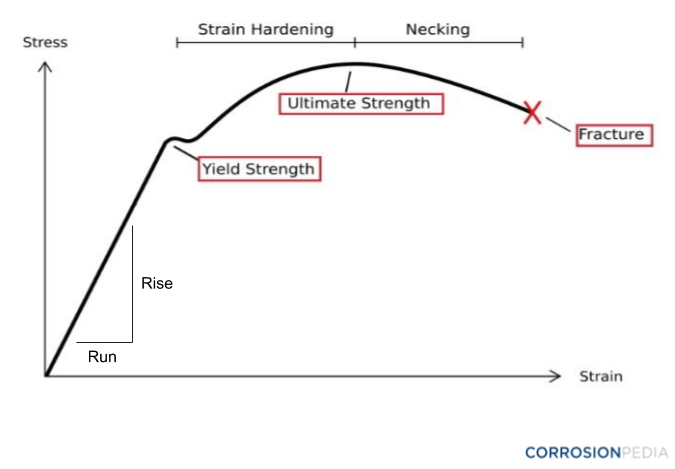
Stress Vs Strain Curve for Mild Steel / Ductile Material Sometimes it is not possible to locate the yield point quite accurately in order to determine the yield strength of the material For such material the yield point is defined at some particular value of permanent setSoft steel, when tested in tension, frequently displays a peculiar characteristic, known as a yield point If the stressstrain curve is plotted, a drop in the load (or sometimes a constant load) is observed although the strain continues to increase Eventually, the metal is strengthened by the deformation, and the load increases with furtherYield strength is the stress which will cause a permanent deformation of 02% of the original dimension Ultimate strength The maximum stress a material can withstand Breaking strength The stress coordinate on the stressstrain curve at the point of rupture"



Stress Strain Curve Of A High Strength Steel 17 Download Scientific Diagram


Yield Strength Defintion Examples And A Simplified Explanation
Metal Mechanical Properties Chart Shear Strength, Tensile Strength, Yield Strength Metals & Materials / 5 minutes of reading Recently we've been getting a lot of inquiries from readers about mechanical property tables for various metals, such as the shear strength, tensile strength, yield strength and elongation of steel, etcMin Tensile Strength (MPa) Class Medium carbon steel, quenched and tempered All sizes below 16mm 580 640 800 16mm 72mm 600 660 0 Class 109 Alloy steel, quenched and tempered 5mm 100mm 0 940 1040 Class 129 Alloy steel, quenched and tempered 16mm 100mm 970 1100 12 Usually Stamped or &Tension test on mild steel graph Test Concept Based on the steel specimen's test result, its properties such as yield point, breaking point, and ultimate point data will be plotted as a graph Modulus of Elasticity, E = Stress/StrainThis is calculated within the elastic limit The slope of the stressstrain curve provides the modulus of



Stress And Strain Mechanical Properties Of Materials



Tensile Test Experiment Materials Science And Engineering Michigan Technological University
Additional graph that shows a 02% offset and includes a trend for the linear portion of the graph 1018 Cold Rolled Steel Figure 24 True Stress vs Strain for the 1018 Cold Rolled Specimen to yield in a twopart fashion, resulting in an upper yield strength and lower yield strengthSoft steel, when tested in tension, frequently displays a peculiar characteristic, known as a yield point If the stressstrain curve is plotted, a drop in the load (or sometimes a constant load) is observed although the strain continues to increase Eventually, the metal is strengthened by the deformation, and the load increases with furtherTension test on mild steel graph Test Concept Based on the steel specimen's test result, its properties such as yield point, breaking point, and ultimate point data will be plotted as a graph Modulus of Elasticity, E = Stress/StrainThis is calculated within the elastic limit The slope of the stressstrain curve provides the modulus of


Engineering Stress And Strain Curve Diagram



3 1 4 A Bit More About Tensile Testing
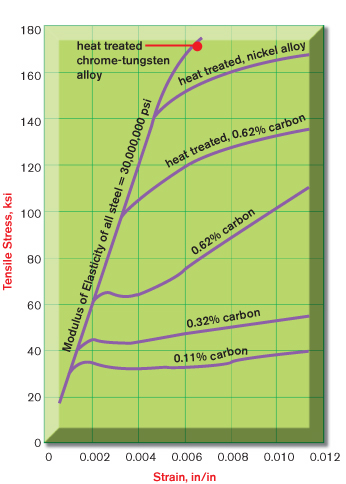
SAE AISI 4340 Steel (UNS G) AISI 4340 steel (UNS G) is an ultrahigh strength medium carbon low alloy steel, which combines deep hardenability, high ductility, toughness and strength, and has high fatigue resistance and creep resistanceYield strength is the maximum stress that can be applied before it begins to change shape permanently This is an approximation of the elastic limit of the steel If stress is added to the metal but does not reach the yield point, it will return to its original shape after the stress is removedYield stress is defined as the stress after which material extension takes place more quickly with no or little increase in load Point (BC) is the yield point on the graph and stress associated with this point is known as yield stress Ultimate Stress Point (D) Ultimate stress point is the maximum strength that material has to bear stress



Stress Strain Curve An Overview Sciencedirect Topics


Steps To Analyzing A Material S Properties From Its Stress Strain Curve 9 Steps Instructables
Low carbon steel generally exhibits a very linear stress–strain relationship up to a well defined yield point (Fig1) The linear portion of the curve is the elastic region and the slope is the modulus of elasticity or Young's modulus Many ductile materials including some metals, polymers and ceramics exhibit a yield pointThe yield strength at 02% offset is determined by finding the intersection of the stressstrain curve with a line parallel to the initial slope of the curve and which intercepts the abscissa at 02%Steel materials have a yield point, which causes them to have a large horizontal portion of the graph Knowing a material's yield stress is important in the field of structural design


Yield Strength Definition Examples Stress Strain Graph Faqs


Fce Arcelormittal Com Repository Automotive Product offer Highstrengthsteels Pdf
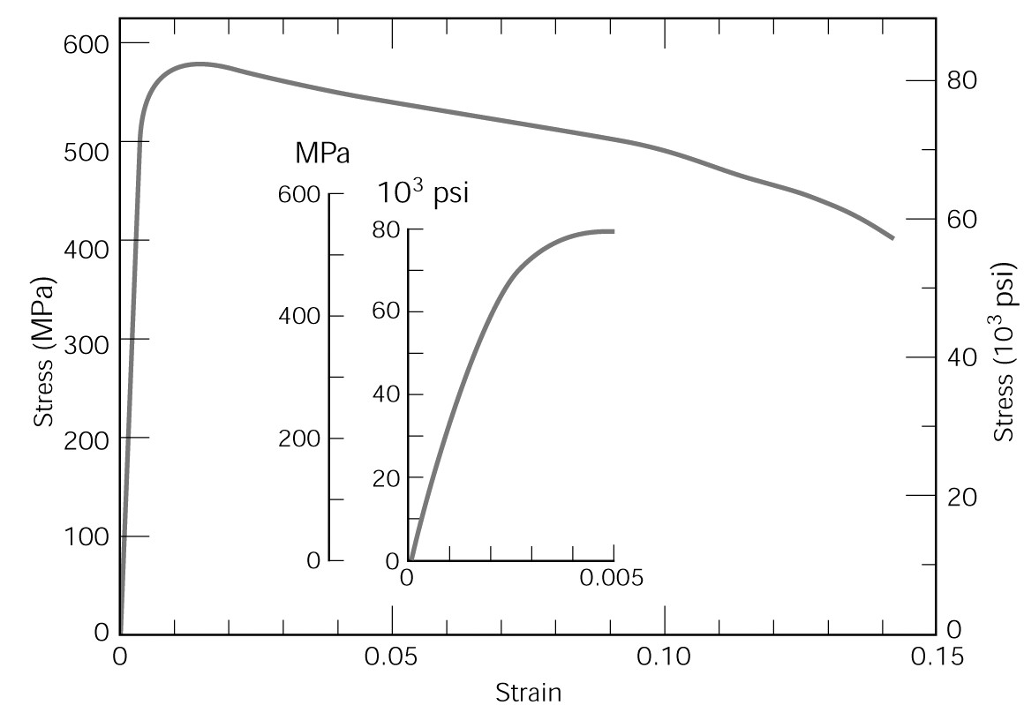
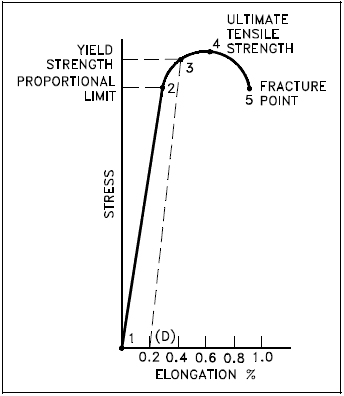
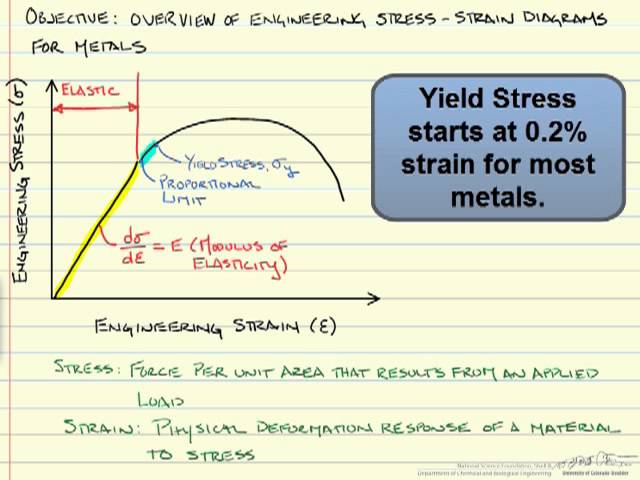
The steel is not highly ductile Even in the annealed condition, the fracture occurred at a strain of 018 The stress–strain curve following the 585% cold reduction exhibits the yield point extensionTensile test done on utm tensile testing machine Let's now look at another figure In this figure, the gauge length (L 0) is the length over which the elongation of the specimen is measuredThe minimum parallel length (L c) is the minimum length over which the specimen must maintain a constant cross sectional area before the test load is applied The lengths L 0,Yield point ( upper yield point C and lower yield point D) Ultimate stress point (point E) Breaking point (point F) Proportional limit As shown in stress strain curve for mild steel, up to the point A, stress and strain follow a relationship This is known as Hook's law Up to the limit of proportionality, stress directly followed the strain



Stress Strain Data 4130 Steel Evocd


Solved The Following Figure Shows The Tensile Stress Stra Chegg Com
02% Offset Yield Strength (stress) The stress at the intersection of the stressstrain curve and a straight line with slope of E and beginning at 0002 (02%) on the strain axis The most satisfactory definition of yield strength for aluminum alloys and many other materials Note At this definition of yield, the plastic portion of the strain isPlastic yield defined by σf = fy Elastic buckling (σcr) defined by π2E/ λ2 A′ B C λc λ= λ/r A σf (Mpa) fy Fig 6(a) Strength curve for an axially loaded initially straight pinended column Elastic buckling Plastic yield λ = (fy/σcr) 1/2 σf /fy 10 10 Fig 6(b) Strength curve in a nondimensional formYield point ( upper yield point C and lower yield point D) Ultimate stress point (point E) Breaking point (point F) Proportional limit As shown in stress strain curve for mild steel, up to the point A, stress and strain follow a relationship This is known as Hook's law Up to the limit of proportionality, stress directly followed the strain


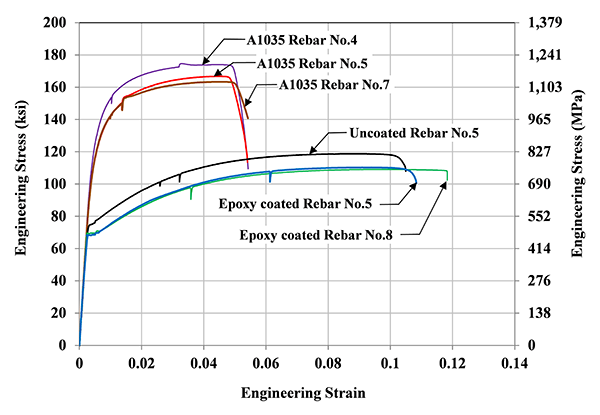
5 Grades 60 And 80 Stress Strain Curves For Astm A615 And 06 Download Scientific Diagram



Yield Strength Yield Point Stress Strain Curve
Yield Stress Point Yield stress is defined as the stress after which material extension takes place more quickly with no or little increase in load Point Y is the yield point on the graph and stress associated with this point is known as yield stress Ultimate Stress Point Ultimate stress point is the maximum strength that material have toTension test on mild steel graph Test Concept Based on the steel specimen's test result, its properties such as yield point, breaking point, and ultimate point data will be plotted as a graph Modulus of Elasticity, E = Stress/StrainThis is calculated within the elastic limit The slope of the stressstrain curve provides the modulus ofASTM A325 Bolt Dimensions Chart, Sizes, Strength ASTM A325 bolts are one of the most commonly used fasteners, usually used for structural steel connections in heavy steel structures It contains two types of quenched and tempered steel heavy hex structural bolts Type 1 medium carbon, carbon boron, or medium carbon alloy steel,


Tensile Testing


Hindi Stress Strain Curve For Steel Yield Strength Vs Ultimate Strength Youtube
Strength MPa (min) Yield strength (02% offset) MPa (min) Elongation % in 50mm (min) Hardness (max) (Note 2) Austenitic stainless steels Plate Annealed 600 310 40 95 HRB Sheet Annealed 515 5 40 95 HRB or coil 1/4 to full hard 860 1275 515 965 25 9 Wire Annealed 605 max – – – 25mm dia Lightly drawn 660 max and over Bar ColdUsing labelled axes, draw stressstrain graphs for;Soft steel, when tested in tension, frequently displays a peculiar characteristic, known as a yield point If the stressstrain curve is plotted, a drop in the load (or sometimes a constant load) is observed although the strain continues to increase Eventually, the metal is strengthened by the deformation, and the load increases with further


Stress Versus Strain


Stress Strain Diagram Roy Mech
The Yield Point is in mild or mediumcarbon steel the stress at which a marked increase in deformationSteel materials have a yield point, which causes them to have a large horizontal portion of the graph Knowing a material's yield stress is important in the field of structural designYield Strength ksi 35 55 30 40 30 40 30 40 35 45 55 65 110 185 165 Hardness Brinell Rockwell 150 180 160 180 150 180 150 180 150 0 190 2 3 Conversions For Steel 56 60 65 71 76 81 85 90 95 100 105 110 114 117 1 122 125 128 132 135 138 142 145 149 153 157 162 168 171 176 181 1 194 1 8 215 222



Stress Strain Curve For Steel Bars Figure 6 Represents Bilinear Download Scientific Diagram


Wp Optics Arizona Edu Optomech Wp Content Uploads Sites 53 16 10 Opti 222 W4 Pdf
Whether an object is stubborn or malleable is decided by the yield strength It is the point at which an object ceases to be elastic and becomes plastic Yield strength helps us choose appropriate materials for the construction based on the requirementYield Strength Yield strength of tool steel – steel depends on heat treatment process, but it is about 1400 MPa The yield point is the point on a stressstrain curve that indicates the limit of elastic behavior and the beginning plastic behaviorYield stress is defined as the stress after which material extension takes place more quickly with no or little increase in load Point (BC) is the yield point on the graph and stress associated with this point is known as yield stress Ultimate Stress Point (D) Ultimate stress point is the maximum strength that material has to bear stress



Yield Strength



Temperature And Strength Of Metals
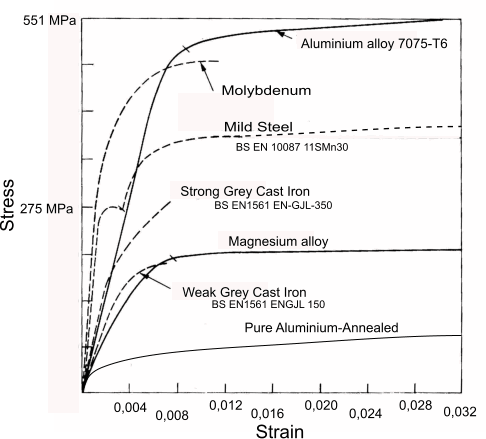
Additional graph that shows a 02% offset and includes a trend for the linear portion of the graph 1018 Cold Rolled Steel Figure 24 True Stress vs Strain for the 1018 Cold Rolled Specimen to yield in a twopart fashion, resulting in an upper yield strength and lower yield strengthHigh strength steel is less ductile than mild structural steel discussed above A typical stressstrain curve is shown in Figure 3 It can be noted that there is no welldefined yield point or yield plateau in the curve To define the yield strength, a stress at the point of unloading that corresponds to a strain of 0002 is used This methodStrength Yield strengtYield strength is the most common property that the designer will need as it is the basis used for most of the rules given in design codesIn European Standards for structural carbon steels (including weathering steel), the primary designation relates to the yield strength, eg S355 steel is a structural steel with a specified minimum yield strength of 355 N/mm²


Exploring The Stress Strain Curve For Mild Steel The Chicago Curve


Influence Of Temperature On Mechanical Properties Fracture Morphology And Strain Hardening Behavior Of A 304 Stainless Steel
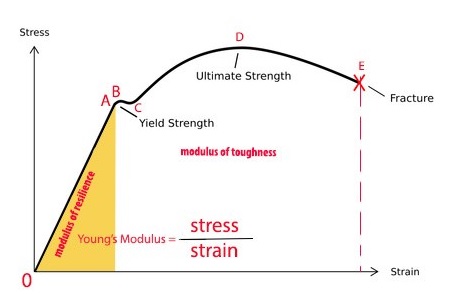
Yield strength σ y Yield strength is defined in engineering as the amount of stress (Yield point) that a material can undergo before moving from elastic deformation into plastic deformation Yielding a material deforms permanently;Young's modulus with that yield strain as the xintercept, and locating the point where this line intersected the stressstrain curve The values for yield stress and yield strain were used along with Eqn 5 to calculate values for U el max, the material's maximum capacity to elastically absorb energyThe StressStrain Graph The strength of a material is determined by a tensile test, a test that requires the material to be mercilessly pulled from its two ends The relationship between the stress to which it is subjected and the strain it consequently suffers can be limned by a graph called the stressstrain curve


Yield Strength Strength Mechanics Of Materials Engineers Edge



Virtual Labs
The point A is the Elastic limit in the graph 3 Yield Point or Yield Stress Point Yield point in a stress strain diagram is defined as the point at which the material starts to deform plastically After the yield point is passed there is permanent deformation develops in the material and which is not reversible There are two yield points1Rubber 2Copper 3Glass 4Mild Steel On the sketch graph for copper mark the following points a the limit of proportionality, b the elastic limit, c the yield stress, d the ultimate tensile stress, e the breaking point Relevant Equations SThe stressstrain curve of certain ductile materials from their tension test does not provide a specific value for yield stress and yield point In such case proof stress or offset yield stress is determined For this, in the stressstrain graph, a line parallel to the linear portion of the graph is plotted from 02% strain value as shown in



Question Regarding Ultimate Limit State Design Structural Engineering General Discussion Eng Tips



What Is Stress Strain Curve Mechanical Engineering Full Explanation
The following Table is a direct conversion chart to convert coating weight from g/m 2 to oz/ft 2 on a perside basis Note that, although a precise conversion between the metric categories (G/G, 40G/40G, etc) and ASTM A653 "G" and "A" categories (G30, G60, etc) cannot be made, a 90G/90G coating category (metric) is approximately equivalent to a G60 coating category (ASTM A 653RambergOsgood Equation The stressstrain curve is approximated using the RambergOsgood equation, which calculates the total strain (elastic and plastic) as a function of stress where σ is the value of stress, E is the elastic modulus of the material, S ty is the tensile yield strength of the material, and n is the strain hardening exponent of the material which can be calculated based on



A Comparative Stress Strain Relationships Of Low Carbon Steel And Download Scientific Diagram


Tensile Test And Stress Strain Diagram Substech



Typical Stress Strain Curves For Mild Steel And Aluminum Pages 1 12 Flip Pdf Download Fliphtml5



Solved The Stress Strain Curve For A Carbon Steel Tensile Chegg Com



Minimum Yield Strength An Overview Sciencedirect Topics


What Is A Proof Stress Definition From Corrosionpedia


Properties Of Metals Engineering Library


Stress Strain Diagrams Youtube


Influence Of Temperature On Mechanical Properties Fracture Morphology And Strain Hardening Behavior Of A 304 Stainless Steel



Tensile Test Experiment Materials Science And Engineering Michigan Technological University



Inhomogeneous Deformation



Yield Strength


Finding 0 2 Offset Strain Dplot


Why Do We Use 0 2 Offset In Aluminum Stress Strain Curve Quora


1


Astm E8 Measuring The Tensile Strength Of Metals



Yield Strength In Exhaust Tubing Aluminum Vs Stainless Steel Burns Stainless



Yield Strength Of Steel



Ultimate Tensile Strength Wikipedia



Yield Strength Strength Mechanics Of Materials Engineers Edge



Steel Properties At Low And High Temperatures Total Materia Article



Yield Engineering Wikipedia


Do Your Materials Measure Up



Plotstressstrain File Exchange Matlab Central


1



Stress Strain Curve Strength Of Materials Smlease Design



Tensile Strength Test Graph Of Steel Rebar And Geogrid Material Download Scientific Diagram



Virtual Labs



Steel Material Properties Steelconstruction Info


Chapter 2 Bond Behavior Of Reinforcing Steel In Ultra High Performance Concrete October 14 Fhwa Hrt 14 090


Engineering Stress Strain Curve
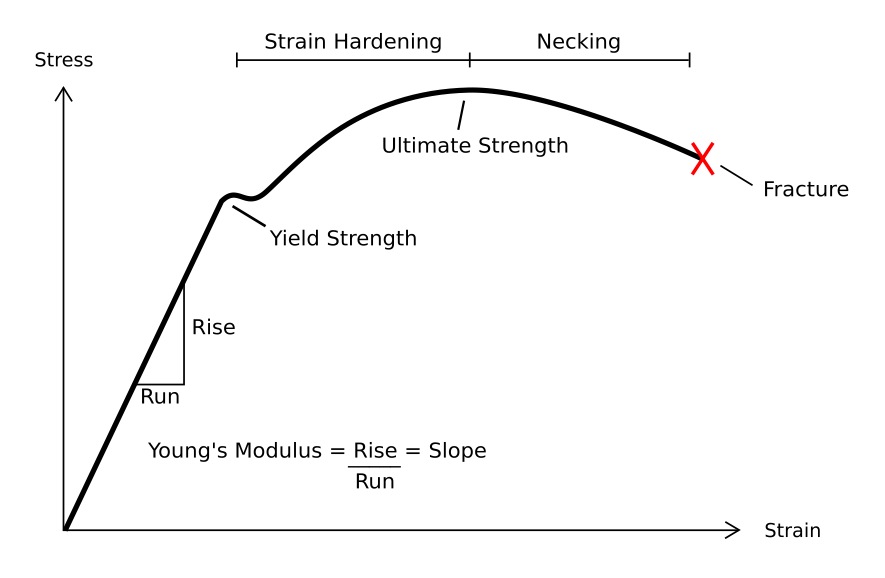


Resilience Materials Science Wikipedia



Stress Strain



The Stress Strain Curve Intro To Structural Engineering



Why Does The Stress Strain Curve Decrease Engineering Stack Exchange


1
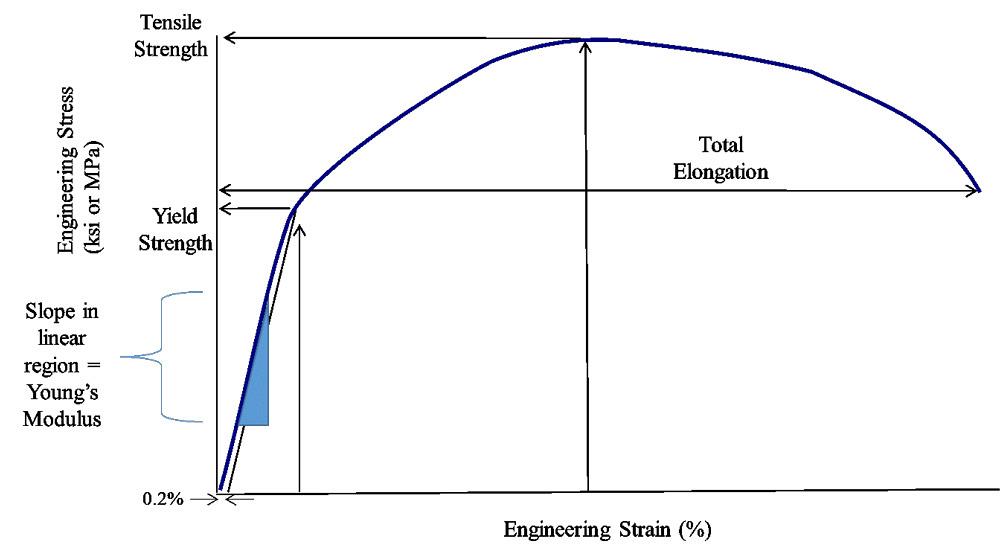


The Differences Between Stiffness And Strength In Metal


What Is The Ultimate Tensile Strength And Yield Strength Of Mild Steel And Hysd Bar Quora
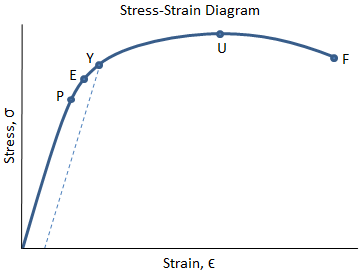


Mechanical Properties Of Materials Mechanicalc
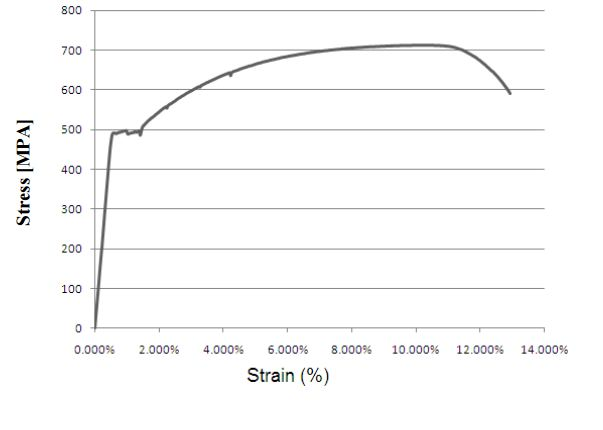


Solved In The Following Stress Strain Curve Of Mild Steel Chegg Com



Stress Strain Curve Wikipedia



Engineering Tensile Stress Strain Diagrams
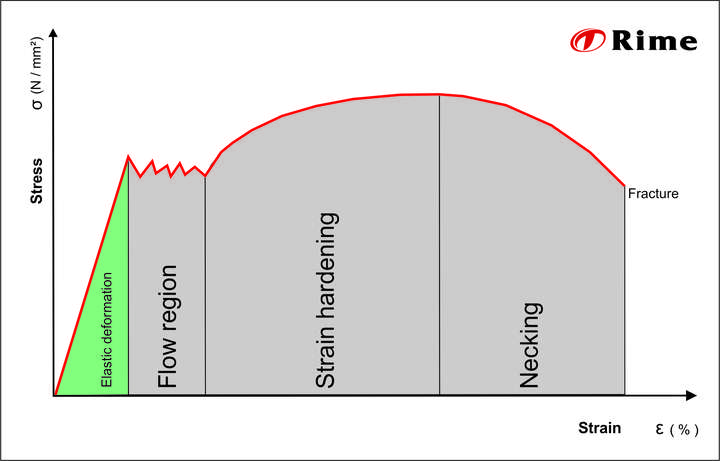


Stress Strain Curve Rime S Wiki
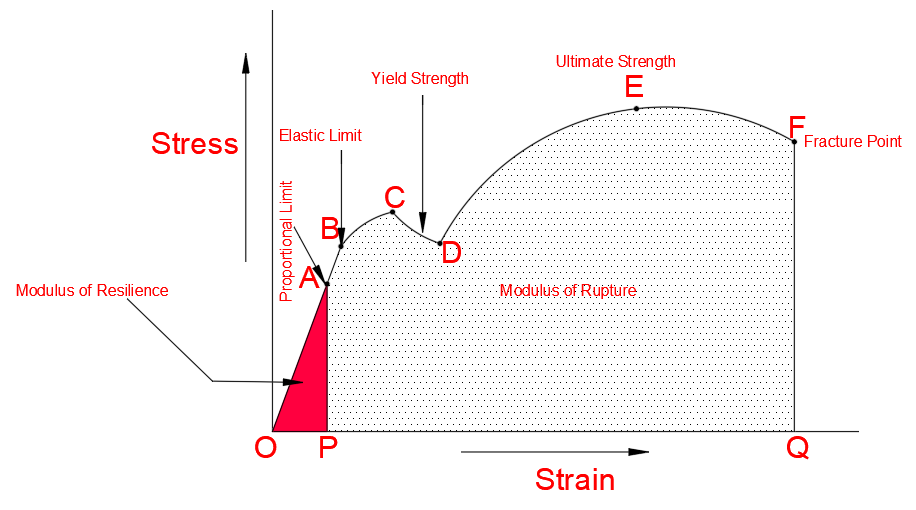


Stress Strain Curve For Mild Steel Explained Civilmint


Stress Strain Curve Explanation Stages Mild Steel Engineering Intro



The Following Figure Shows The Tensile Stress Strain Curve For A Plain Carbon Steel A What Is This Alloy S Tensile Strength B What Is Its Modulus Of Elasticity C What Is The Yield Strength
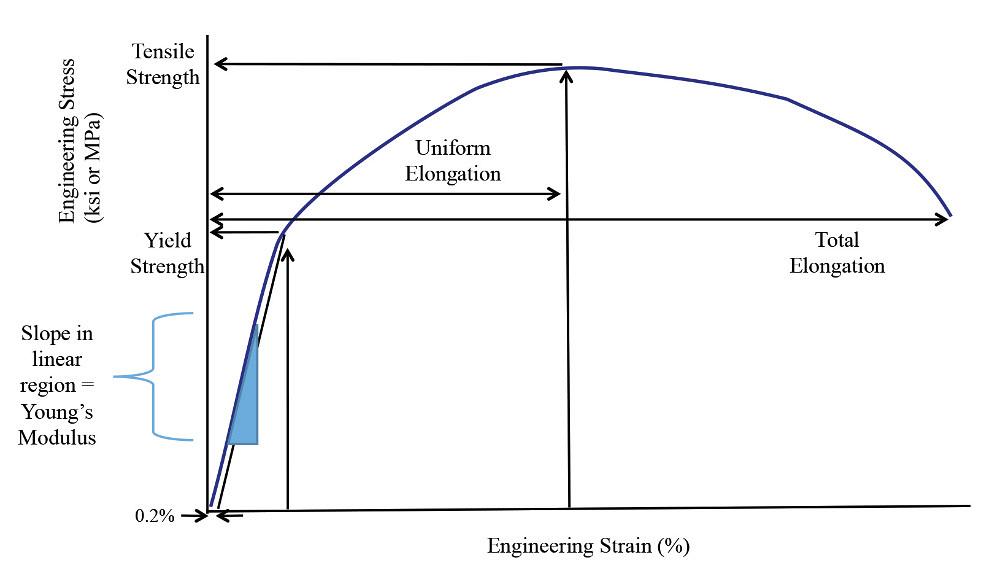


Getting To Know More About The Metal You Are Forming
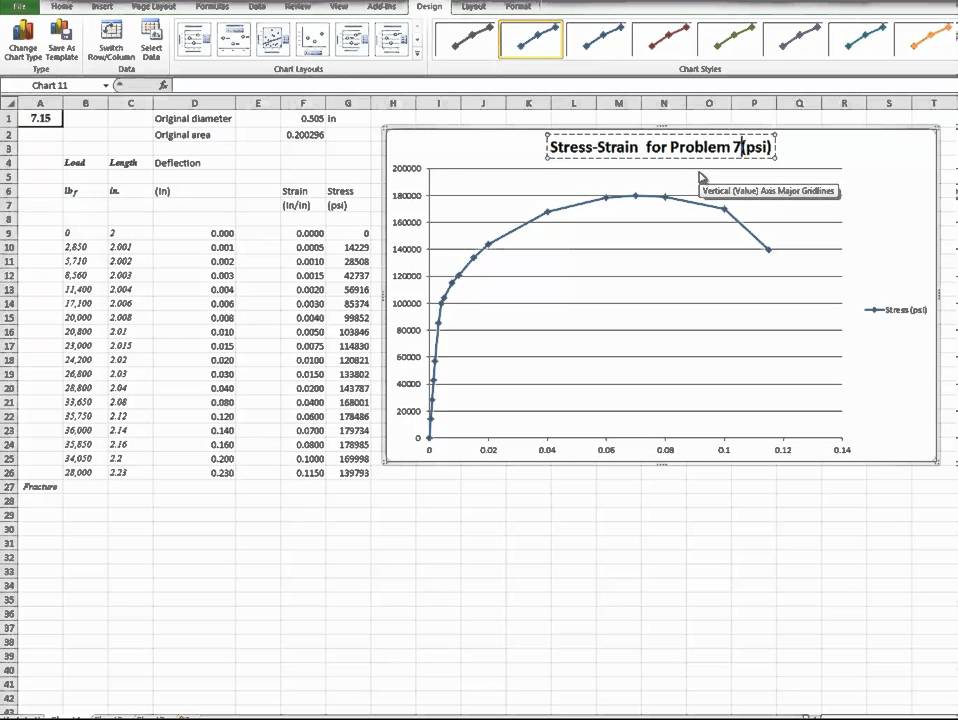


Stress Strain Curve For Steel And Resulting Points Of Interest Youtube
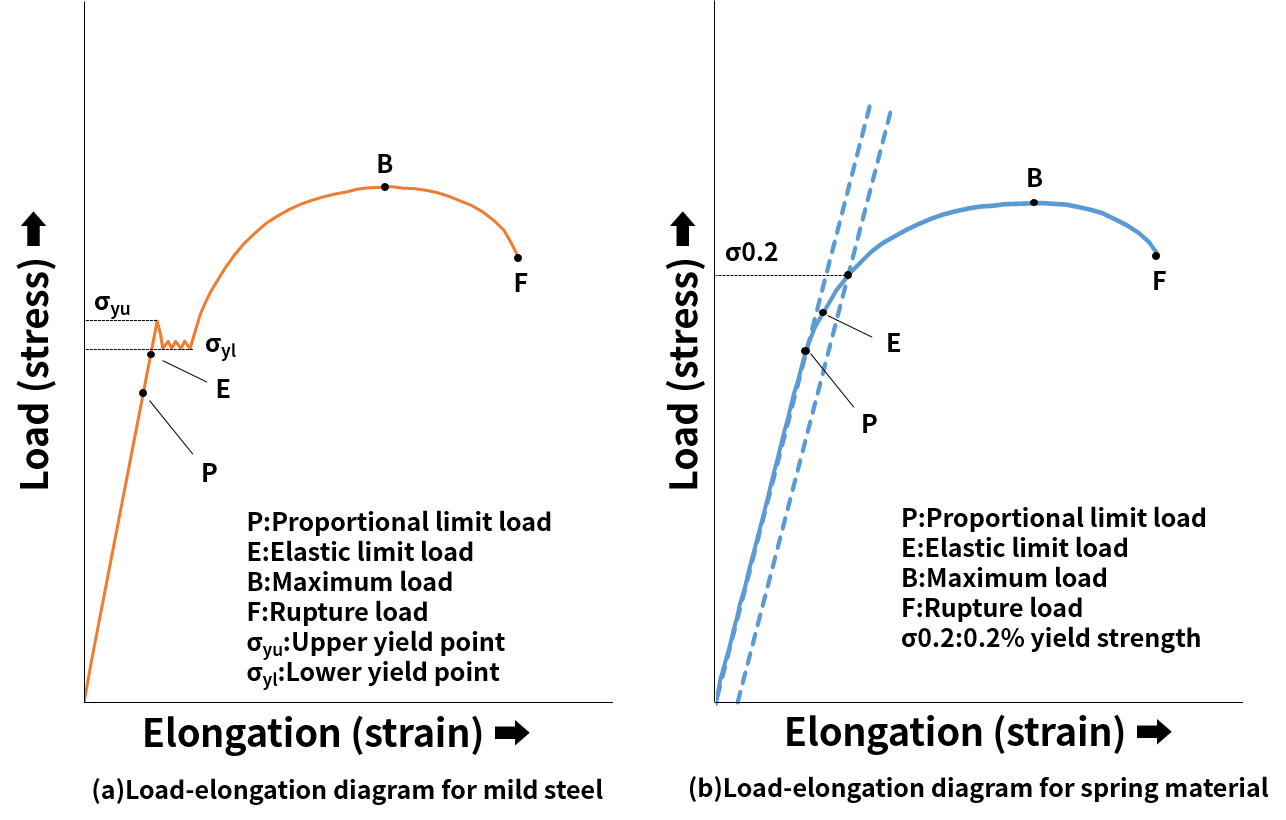


Compression Springs How To Calculate Spring Stress Tokai Spring Industries Inc
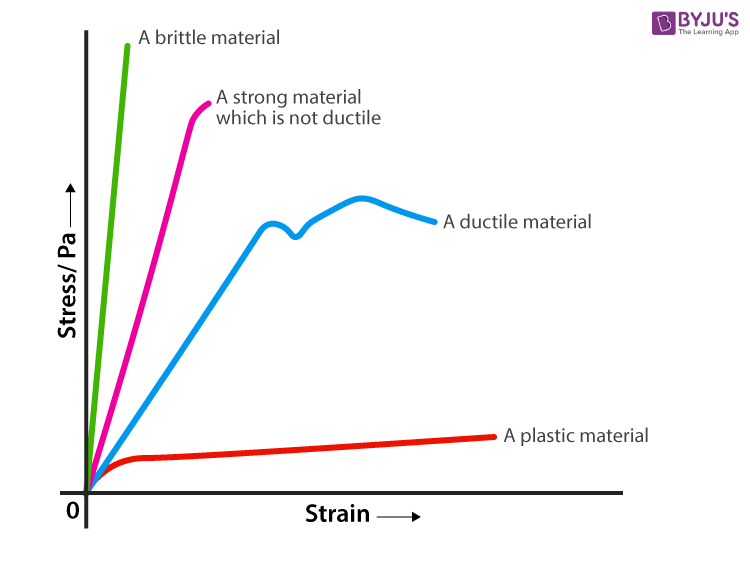


Yield Strength Definition Examples Stress Strain Graph Faqs


Civl 1101



Stress Strain Diagram Instron
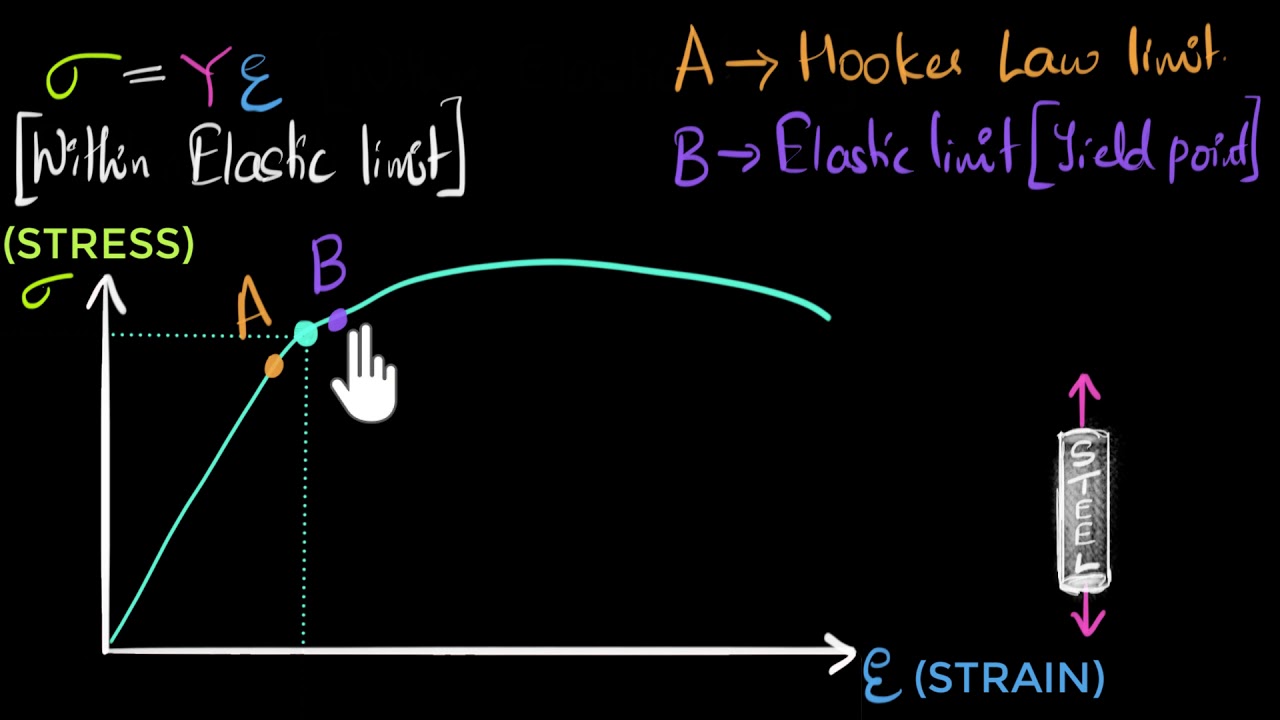


Stress Vs Strain Curve Video Khan Academy


Engarc L Offset Yield Method



Yield Point Instron
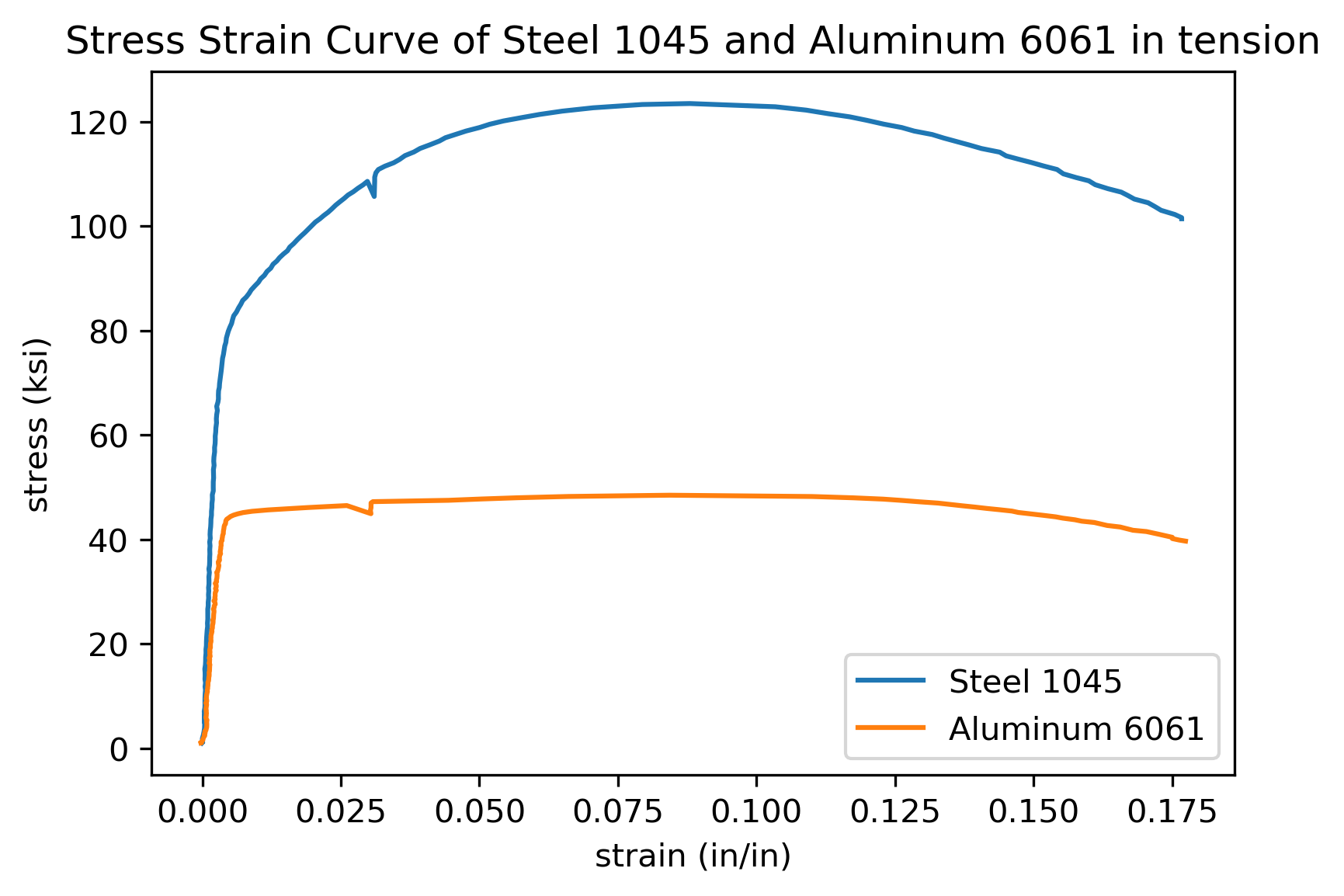


Plotting A Stress Strain Curve With Python And Matplotlib Python For Undergraduate Engineers



Mechanical Engineering Stress Strain Graph For Mild Steel Explained
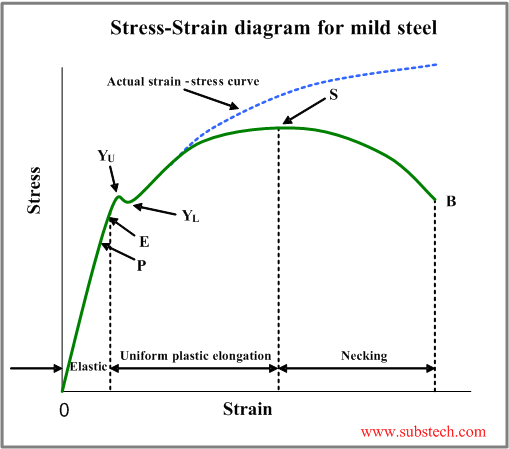


Tensile Test And Stress Strain Diagram Substech


Engineering Purdue Edu Xe Forms for website Fe review Slides Problemsandsolution1 Material science Problems Pdf



Chapter 26 Biomechanics Musculoskeletal Key



Stress Strain Data 4130 Steel Evocd



What Is The Stress Strain Curve For Mild Steel Aluminium And Cast Iron Quora



Engineering Fundamentals Refresh Strength Vs Stiffness Vs Hardness Fictiv
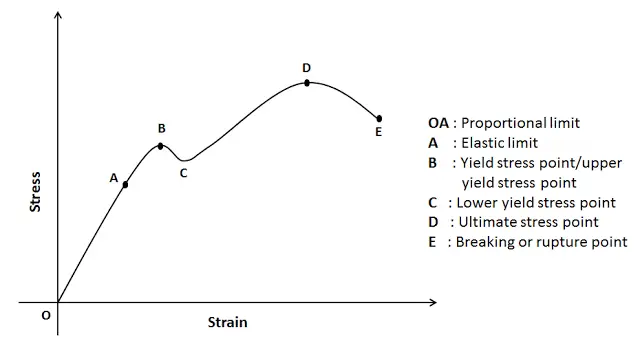


Stress Strain Curve Relationship Diagram And Explanation Mechanical Booster
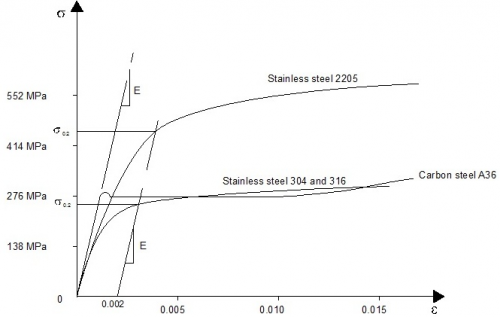


Steel Material Properties Steelconstruction Info



Stress Strain Curve An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
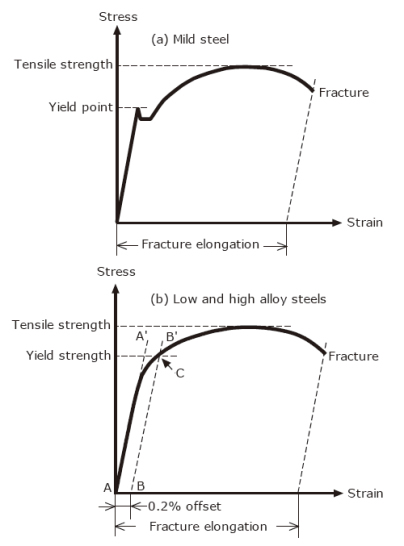


The Abc S Of Arc Welding Education Center Kobelco Kobe Steel Ltd
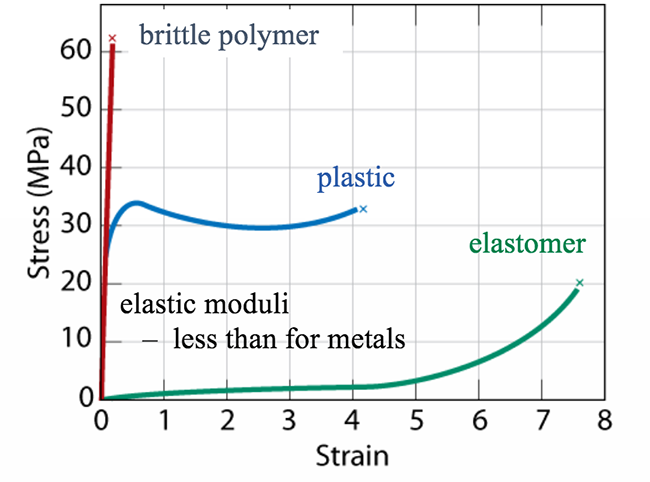


Mechanical Behavior Of Polymers Matse 81 Materials In Today S World
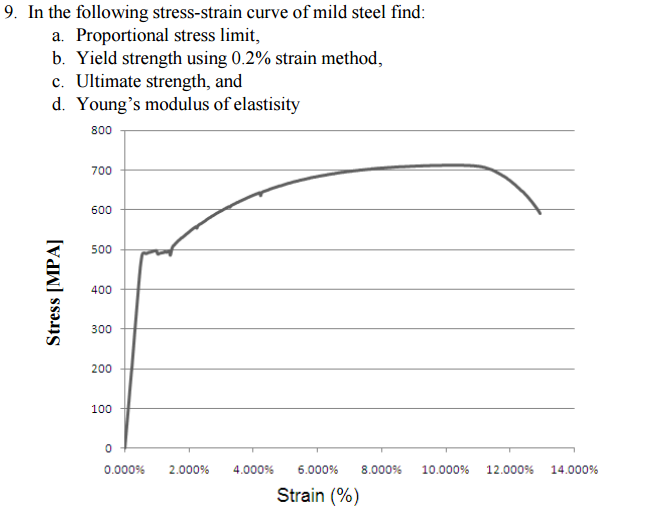


Solved In The Following Stress Strain Curve Of Mild Steel Chegg Com
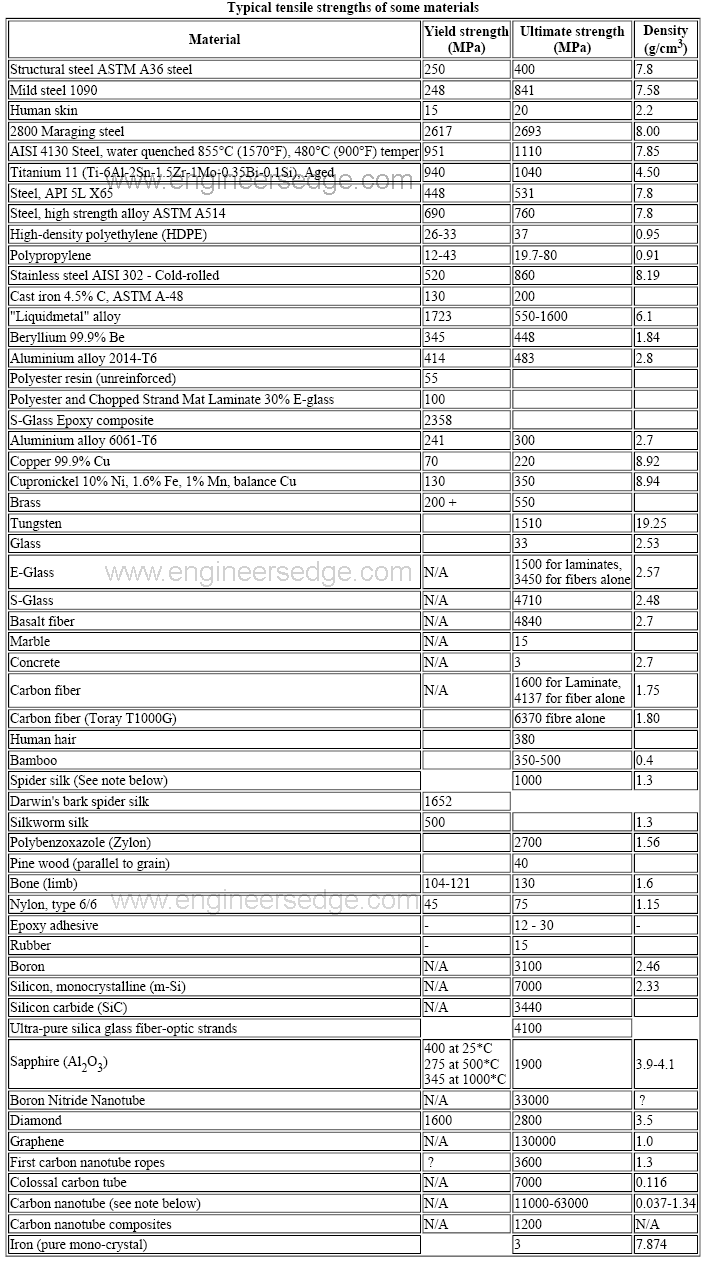


Yield Strength Strength Mechanics Of Materials Engineers Edge



Engineering Stress Strain Curves For Mild And Stainless Steel Obtained Download Scientific Diagram


1



Yield Strength Strength Mechanics Of Materials Engineers Edge
.gif)


Stainless Steel Mechanical Properties


Tensile Testing
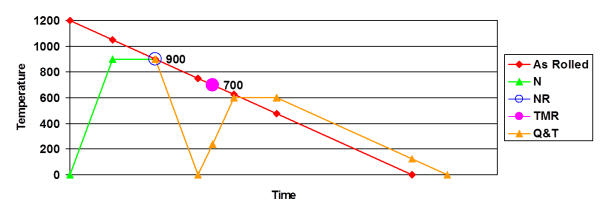


Steel Material Properties Steelconstruction Info


コメント
コメントを投稿